electron cloud diagram|Khan Academy : Tagatay Atomic orbital - Wikipedia 用於課程計劃和班級管理的 Dynos 教師 LMS 應用程序CSGO500 - $5 Gift Card | Buy cheap on Kinguin.net
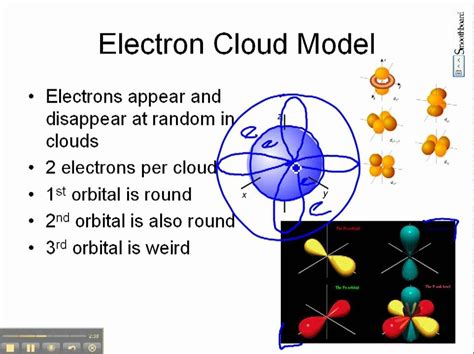
electron cloud diagram,Learn about electron cloud model, where is the electron cloud located, who discovered the electron cloud and its theory along with diagram.
The electron cloud is a cloud of probability surrounding the nucleus in an atom where one has the highest probability of finding an electron. When you think of an .In quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in an atom. This function describes the electron's charge distribution around the atom's nucleus, and can be used to calculate the probability of finding an electron in a specific region around the nucleus. Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a set of values of the three quantum numbersWhat Is an Electron Cloud? - ThoughtCoAtomic orbital - WikipediaElectron Cloud | Definition, Model & Theory - Lesson | Study.comWhat Is The Electron Cloud Model? - Universe Today What is an electron cloud? Learn the definition of electron and electron cloud, learn about the electron cloud model, and view an electron cloud diagram. .

Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, .

Updated on December 08, 2019. An electron cloud is the region of negative charge surrounding an atomic nucleus that is associated with an atomic orbital. It is defined mathematically, describing a region with a .Khan AcademyUpdated on December 08, 2019. An electron cloud is the region of negative charge surrounding an atomic nucleus that is associated with an atomic orbital. It is defined mathematically, describing a region with a .Explore the complex world of atoms with our in-depth guide on electron clouds and atomic orbitals. Learn how electrons are arranged in atoms and how they aff.
Khanmigo is now free for all US educators! Plan lessons, develop exit tickets, and so much more with our AI teaching assistant.
An electron cloud is an electron density diagram. It shows the probability of finding electrons in certain regions around the nucleus.Electron cloud is an informal way to describe an atomic orbital.. The electron cloud is not really a thing. An electron cloud model is different from the older Bohr atomic model by Niels Bohr.Bohr talked about electrons orbiting the nucleus. Explaining the behavior of these electron "orbits" was a key issue in the development of quantum mechanics. [1] . A crash course in electron behavior.—More on the Atomic Model | Wiki—"In quantum mechanics, an atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the w. At ordinary temperatures, the electron in a hydrogen atom is almost invariably found to have the lowest energy available to it. That is, the electron occupies the 1s orbital. The electron cloud looks like the dot-density diagram shown in Figure 1 from Electron Waves in the Hydrogen Atom. The modern model is also commonly called the electron cloud model. That’s because each orbital around the nucleus of the atom resembles a fuzzy cloud around the nucleus, like the ones shown in the Figure below for a helium atom. The densest area of the cloud is where the electrons have the greatest chances of being.The electron orbital simulator (EOS) is a Unity program that serves as a visual aid for learning the structure of the atom. On the left is a 3D model of the atom selected in the periodic table. Using the dropdown, you may view a simplified model of it's electron cloud or a 3D representation of the bohr model.
The Role of the Electron Cloud in Atomic Structure. The electron cloud plays a crucial role in the way that atoms are structured. The arrangement of electrons in an atom determines many of the .
In 1913, the Danish physicist Niels Bohr proposed a model of the electron cloud of an atom in which electrons orbit the nucleus and were able to produce atomic spectra. Understanding Bohr's model requires some knowledge of electromagnetic radiation (or light). . Figure \(\PageIndex{10}\) A shell diagram of lithium (left) and Sodium (right)electron cloud diagram In contrast, electrons are found outside the nucleus in a region called the electron cloud or electron shell. 1) Electrons. They are negatively charged particles that revolve around the nucleus in a fixed orbit. Unlike protons and neutrons, electrons are fundamental particles much smaller (almost 1800 times) in size than protons and neutrons.
Pauli Exclusion Principle. The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons can have the same four quantum numbers. The first three (n, l, and m l) may be the same, but the fourth quantum number must be different. A single orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, which must have opposing spins; otherwise they would have the same four . Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The diagram of an electron configuration specifies the subshell (n and l value, with letter symbol) and superscript number of electrons. The Aufbau Principle. To determine the electron configuration for any particular atom, we can “build” the structures in the order of atomic numbers. Beginning with hydrogen, and .
The 1s orbital at the bottom of the diagram is the orbital with electrons of lowest energy. The energy increases as we move up to the 2s and then 2p, 3s, and 3p orbitals, showing that the increasing n value has more .Another way of thinking about the electron energy levels is that they are the energies needed to remove that electron from the atom or to move an electron to a “higher” orbital. Conversely, this is the same amount of energy released when an electron moves from a higher energy to a lower energy orbital.
Figure \(\PageIndex{2}\): The diagram of an electron configuration specifies the subshell (n and l value, with letter symbol) and superscript number of electrons. The Aufbau Principle. To determine .Electron orbital diagrams are diagrams used to show the energy of electrons within the sublevels of an atom or atoms when used in bonding. Single atom diagrams (atomic orbital diagrams) consist of horizontal lines or boxes for each sublevel. Within orbitals, arrows indicate the spin direction of the occupant electrons. .
Electron configuration diagrams poster (atomic number top) A3 PDF, Size 5.34 mb; Electron configuration diagrams poster (atomic number bottom) A4 single pages PDF, Size 5.38 mb; Electron configuration diagrams poster (atomic number bottom) A3 PDF, Size 5.75 mb; Electron configuration diagrams fact sheet Editable handout | .electron cloud diagram Khan Academy The electron configuration of helium refers to the arrangement of electrons in the helium atom’s orbitals. It describes how electrons are distributed among the various atomic orbitals and energy levels, and provides a detailed map of where each electron is likely to be found. The electron configuration of all the elements can be done through the orbital diagram. Electron configuration of bromine through orbital. Atomic energy shells are subdivided into sub-energy levels. These sub-energy levels are also called orbital. The most probable region of electron rotation around the nucleus is called the orbital.
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
electron cloud diagram|Khan Academy
PH0 · What Is an Electron Cloud?
PH1 · What Is The Electron Cloud Model?
PH2 · The Electron Cloud Model explained
PH3 · Khan Academy
PH4 · Electron Cloud: Definition, Model, Explanation And Examples
PH5 · Electron Cloud: Definition and Diagram
PH6 · Electron Cloud — Definition & Overview
PH7 · Electron Cloud & Atomic Orbital: Understanding the
PH8 · Electron Cloud
PH9 · Atomic orbital